Note
Click here to download the full example code
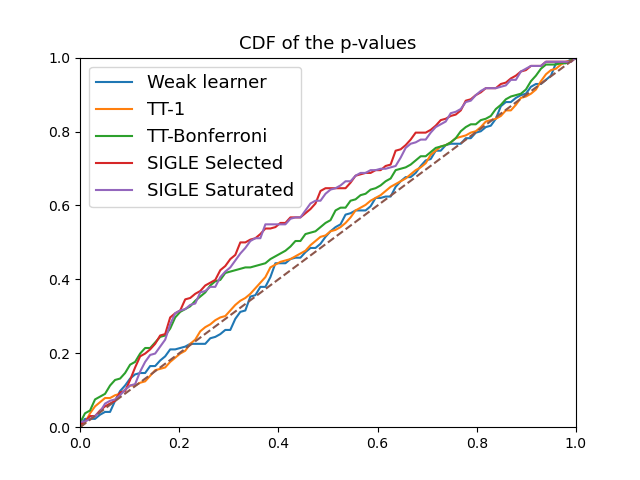
CDF of p-values#
The example shows the cumulative disribution function (CDF) of the p-values of different post-selection inference methods for a composite hypothesis testing problem with a global null.
import PSILOGIT
import numpy as np
from PSILOGIT.tools import *
from sklearn.linear_model import LogisticRegression, LogisticRegressionCV
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
Choice of the signal strength
nu = 0.1
Choice of the type of alternative (localized or disseminated)
modes = ['disseminated-signal' ,'localized-signal']
mode = modes[0]
Choice of the number of steps for the rejection sampling method
nb_ite = 100000
Definition of the experiment.
if mode=='localized-signal':
vartheta = np.zeros(10)
vartheta[0] = nu
else:
vartheta = nu*np.ones(10)
model = PSILOGIT.PSILOGIT(truetheta=vartheta, regularization=2, n=100, p=10)
print('Size of the set of active variables: ', len(model.M))
Size of the set of active variables: 7
Sampling states according to the conditional distribution using the rejection sampling method.
0%| | 0/100000 [00:00<?, ?it/s]
Sampling states according to the conditional distribution using the rejection sampling method under the global null.
0%| | 0/100000 [00:00<?, ?it/s]
p-values for the SIGLE procedures#
0%| | 0/260 [00:00<?, ?it/s]
0%| | 0/266 [00:00<?, ?it/s]
0%| | 0/260 [00:00<?, ?it/s]
p-values for the procedures derived from the work of Taylor & Tibshirani#
0%| | 0/266 [00:00<?, ?it/s]
0%| | 0/266 [00:00<?, ?it/s]
0%| | 0/266 [00:00<?, ?it/s]
0%| | 0/266 [00:00<?, ?it/s]
0%| | 0/266 [00:00<?, ?it/s]
0%| | 0/266 [00:00<?, ?it/s]
0%| | 0/266 [00:00<?, ?it/s]
0%| | 0/266 [00:00<?, ?it/s]
p-values for the weak learner#
lspvals_naive = model.pval_weak_learner(statesnull, states, barpi, signull=signull)
0%| | 0/260 [00:00<?, ?it/s]
0%| | 0/266 [00:00<?, ?it/s]
CDF of pvalues#
Total running time of the script: ( 1 minutes 11.583 seconds)